- Battery Manufacturing Equipment
- Battery Laboratory Assembly Equipment
- Battery Pack Assembly Equipment
- Sodium Ion Battery Manufacturing Equipment
- Solid State Cell Production Line
- Dry Electrode Assembly Equipment
- Supercapacitor Assembly Equipment
- Perovskite Solar Cell Lab Equipment
- Li ion Battery Materials
- Ni / Al / Cu Metal Foam
- Customized Electrode
- Cathode Active Materials
- Anode Active Materials
- Coin Cell Parts
- Lithium Chip
- Cylindrical Cell Parts
- Battery Current Collectors
- Battery Conductive Materials
- Electrolyte
- Battery Binder
- Separator and Tape
- Aluminum Laminate Film
- Nickel Strip/Foil
- Battery Tabs
- Graphene Materials
- Cu / Al / Ni / Stainless steel Foil
- Battery Laboratory Equipment
- Li ion Battery Tester
- Battery Safety Tester
- Material Characterization Tester
- Rolling Press Machine
- Electrode Mixer
- Coin Cell Crimping Machine
- Coin Cell Electrode Disc Punching
- Pouch Cell Sealing Machine
- Pouch Cell Stacking Machine
- Pouch Cell Forming Machine
- Pouch Cell Ultrasonic Welder
- Pouch Cell Electrode Die Cutter
- Cylinder Cell Sealing Machine
- Cylinder Cell Grooving Machine
- Electrode Slitting Machine
- Cylinder Cell Winding Machine
- Cylinder Cell Spot Welding Machine
- Electrolyte Filling
- Type Test Cell
- Other Battery Making Machine
- NMP Solvent Treatment System
- Vacuum Glove Box
- Coating Machine
- Lab Furnaces
- Ball Mill
- Laboratory Press
- Laboratory Equipment
- Press Equipment
blog
Pouch Cell pilot Machine
- 2025-04-15
Pouch Cell Pilot Machine: Design, Functionality, and Applications
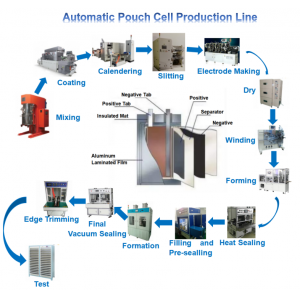
A Pouch Cell Pilot Machine is a semi-automated or fully automated system designed to facilitate the small-scale production of pouch cells (lithium-ion batteries packaged in flexible aluminum-plastic laminated pouches). These machines are used in pilot plants to bridge the gap between laboratory-scale research and full-scale commercial production. They allow manufacturers to test, optimize, and validate manufacturing processes before scaling up to mass production.
Below is a comprehensive overview of pouch cell pilot machines, including their design, functionality, applications, advantages, challenges, and market trends.
---
●1. What Is a Pouch Cell Pilot Machine?
A pouch cell pilot machine is an advanced tool that integrates multiple stages of pouch cell fabrication into a single system. It is designed to produce small batches of pouch cells with high precision and repeatability. The machine operates in a controlled environment, ensuring consistent quality and performance of the cells.
Key features of pouch cell pilot machines:
- Modular design for flexibility.
- Integration of key processes such as stacking, sealing, and testing.
- Scalability to accommodate different cell sizes and chemistries.
---
●2. Key Components of a Pouch Cell Pilot Machine
A typical pouch cell pilot machine consists of the following components:
A. Material Preparation
- Slurry Mixing: Equipment for mixing active materials, binders, and solvents.
- Coating: Machines for applying slurries onto current collectors (aluminum or copper foils).
- Drying: Ovens or dry rooms to remove solvents from coated electrodes.
B. Electrode Processing
- Calendaring: Roll presses to compact electrodes and control thickness.
- Slitting: Cutting electrodes into strips of specific dimensions.
C. Cell Assembly
- Stacking: Automated systems for stacking cathode, separator, and anode layers into a flat structure.
- Lamination: Equipment for inserting the stacked electrodes into pouches made of aluminum-plastic laminate.
- Sealing: Hot pressing or impulse welding machines to seal three sides of the pouch, leaving one side open for electrolyte injection.
D. Electrolyte Injection
- Precision equipment for injecting electrolyte into the pouch through the open side.
E. Final Sealing
- Equipment for sealing the final open side after electrolyte injection.
F. Formation and Testing
- Formation: Controlled charging/discharging cycles to activate the battery.
- Testing: Equipment to evaluate capacity, internal resistance, cycle life, and safety.
G. Environmental Control
- Dry Rooms: Low-humidity environments (<1% RH) to prevent moisture contamination during electrode processing and cell assembly.
---
●3. Operation of a Pouch Cell Pilot Machine
The operation of a pouch cell pilot machine involves several steps:
1. Material Preparation:
- Mix active materials, binders, and solvents to create slurries.
- Coat the slurries onto current collectors using slot-die or blade coating techniques.
2. Electrode Fabrication:
- Dry the coated electrodes in controlled ovens.
- Calender the dried electrodes to achieve desired thickness and density.
- Slit the electrodes into strips of precise dimensions.
3. Cell Assembly:
- Stack the cathode, separator, and anode layers into a flat structure.
- Insert the stacked electrodes into a pouch made of aluminum-plastic laminate.
- Seal three sides of the pouch, leaving one side open for electrolyte injection.
4. Electrolyte Injection:
- Inject electrolyte into the pouch through the open side.
5. Final Sealing:
- Seal the final open side after electrolyte injection.
6. Formation and Testing:
- Perform formation cycles to activate the battery.
- Conduct various tests (e.g., charge/discharge, thermal cycling, short-circuit testing) to evaluate performance and safety.
Pouch Cell Production Line
●4. Applications of Pouch Cell Pilot Machines
A. Process Validation
- Validate manufacturing processes before scaling up to full production.
- Identify bottlenecks or issues in assembly, sealing, or electrolyte injection.
B. Prototype Production
- Produce small batches of pouch cells for testing in electric vehicles (EVs), consumer electronics, or energy storage systems.
C. Quality Assurance
- Ensure consistent quality and performance across batches.
- Identify defects or inconsistencies early in the development process.
D. New Chemistry Development
- Test and optimize new battery chemistries (e.g., solid-state electrolytes, silicon anodes, high-nickel cathodes).
---
●5. Advantages of Pouch Cell Pilot Machines
| Advantage | Description |
|----------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Precision | Enables accurate control over electrode dimensions, stacking, and sealing. |
| Scalability | Provides a platform to scale up from lab-scale experiments to full production. |
| Flexibility | Supports rapid iteration and testing of new materials and designs. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Reduces risks and costs associated with large-scale production. |
| Data Collection | Generates valuable data on cell performance, reliability, and safety. |
---
●6. Challenges in Using Pouch Cell Pilot Machines
A. Equipment Complexity
- Advanced machinery requires skilled operators and regular maintenance.
B. Environmental Control
- Maintaining low-humidity conditions in dry rooms is challenging and costly.
C. Sealing Integrity
- Achieving reliable and leak-free sealing of pouches is critical but difficult.
D. Material Handling
- Ensuring uniform mixing, coating, and drying of electrode materials is essential but challenging.
E. Scalability
- Transferring processes from pilot scale to full production may reveal unforeseen challenges.
---
●7. Market Trends and Future Outlook
A. Increasing Demand for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Growth in electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and portable electronics drives demand for pouch cells.
B. Emerging Technologies
- Solid-state batteries, silicon anodes, and other next-generation technologies are being tested in pouch cell pilot machines.
C. Automation and Digitalization
- Adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies (e.g., IoT, AI, robotics) improves efficiency and reduces costs in pouch cell fabrication.
D. Sustainability
- Focus on recycling and sustainable manufacturing processes is gaining traction.
---
●8. Conclusion
Pouch cell pilot machines are essential tools for advancing battery technology and ensuring successful commercialization. They enable manufacturers to develop, test, and optimize pouch cells in a controlled and efficient manner. While challenges exist, ongoing innovations in equipment, processes, and materials continue to enhance the capabilities of these machines.
If you're planning to set up or operate a pouch cell pilot machine, carefully consider factors such as equipment specifications, environmental control, and scalability. For further details or assistance, feel free to ask!
A Pouch Cell Pilot Machine is a semi-automated or fully automated system designed to facilitate the small-scale production of pouch cells (lithium-ion batteries packaged in flexible aluminum-plastic laminated pouches). These machines are used in pilot plants to bridge the gap between laboratory-scale research and full-scale commercial production. They allow manufacturers to test, optimize, and validate manufacturing processes before scaling up to mass production.
Below is a comprehensive overview of pouch cell pilot machines, including their design, functionality, applications, advantages, challenges, and market trends.
---
●1. What Is a Pouch Cell Pilot Machine?
A pouch cell pilot machine is an advanced tool that integrates multiple stages of pouch cell fabrication into a single system. It is designed to produce small batches of pouch cells with high precision and repeatability. The machine operates in a controlled environment, ensuring consistent quality and performance of the cells.
Key features of pouch cell pilot machines:
- Modular design for flexibility.
- Integration of key processes such as stacking, sealing, and testing.
- Scalability to accommodate different cell sizes and chemistries.
---
●2. Key Components of a Pouch Cell Pilot Machine
A typical pouch cell pilot machine consists of the following components:
A. Material Preparation
- Slurry Mixing: Equipment for mixing active materials, binders, and solvents.
- Coating: Machines for applying slurries onto current collectors (aluminum or copper foils).
- Drying: Ovens or dry rooms to remove solvents from coated electrodes.
B. Electrode Processing
- Calendaring: Roll presses to compact electrodes and control thickness.
- Slitting: Cutting electrodes into strips of specific dimensions.
C. Cell Assembly
- Stacking: Automated systems for stacking cathode, separator, and anode layers into a flat structure.
- Lamination: Equipment for inserting the stacked electrodes into pouches made of aluminum-plastic laminate.
- Sealing: Hot pressing or impulse welding machines to seal three sides of the pouch, leaving one side open for electrolyte injection.
D. Electrolyte Injection
- Precision equipment for injecting electrolyte into the pouch through the open side.
E. Final Sealing
- Equipment for sealing the final open side after electrolyte injection.
F. Formation and Testing
- Formation: Controlled charging/discharging cycles to activate the battery.
- Testing: Equipment to evaluate capacity, internal resistance, cycle life, and safety.
G. Environmental Control
- Dry Rooms: Low-humidity environments (<1% RH) to prevent moisture contamination during electrode processing and cell assembly.
---
●3. Operation of a Pouch Cell Pilot Machine
The operation of a pouch cell pilot machine involves several steps:
1. Material Preparation:
- Mix active materials, binders, and solvents to create slurries.
- Coat the slurries onto current collectors using slot-die or blade coating techniques.
2. Electrode Fabrication:
- Dry the coated electrodes in controlled ovens.
- Calender the dried electrodes to achieve desired thickness and density.
- Slit the electrodes into strips of precise dimensions.
3. Cell Assembly:
- Stack the cathode, separator, and anode layers into a flat structure.
- Insert the stacked electrodes into a pouch made of aluminum-plastic laminate.
- Seal three sides of the pouch, leaving one side open for electrolyte injection.
4. Electrolyte Injection:
- Inject electrolyte into the pouch through the open side.
5. Final Sealing:
- Seal the final open side after electrolyte injection.
6. Formation and Testing:
- Perform formation cycles to activate the battery.
- Conduct various tests (e.g., charge/discharge, thermal cycling, short-circuit testing) to evaluate performance and safety.
Pouch Cell Production Line
●4. Applications of Pouch Cell Pilot Machines
A. Process Validation
- Validate manufacturing processes before scaling up to full production.
- Identify bottlenecks or issues in assembly, sealing, or electrolyte injection.
B. Prototype Production
- Produce small batches of pouch cells for testing in electric vehicles (EVs), consumer electronics, or energy storage systems.
C. Quality Assurance
- Ensure consistent quality and performance across batches.
- Identify defects or inconsistencies early in the development process.
D. New Chemistry Development
- Test and optimize new battery chemistries (e.g., solid-state electrolytes, silicon anodes, high-nickel cathodes).
---
●5. Advantages of Pouch Cell Pilot Machines
| Advantage | Description |
|----------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Precision | Enables accurate control over electrode dimensions, stacking, and sealing. |
| Scalability | Provides a platform to scale up from lab-scale experiments to full production. |
| Flexibility | Supports rapid iteration and testing of new materials and designs. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Reduces risks and costs associated with large-scale production. |
| Data Collection | Generates valuable data on cell performance, reliability, and safety. |
---
●6. Challenges in Using Pouch Cell Pilot Machines
A. Equipment Complexity
- Advanced machinery requires skilled operators and regular maintenance.
B. Environmental Control
- Maintaining low-humidity conditions in dry rooms is challenging and costly.
C. Sealing Integrity
- Achieving reliable and leak-free sealing of pouches is critical but difficult.
D. Material Handling
- Ensuring uniform mixing, coating, and drying of electrode materials is essential but challenging.
E. Scalability
- Transferring processes from pilot scale to full production may reveal unforeseen challenges.
---
●7. Market Trends and Future Outlook
A. Increasing Demand for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Growth in electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and portable electronics drives demand for pouch cells.
B. Emerging Technologies
- Solid-state batteries, silicon anodes, and other next-generation technologies are being tested in pouch cell pilot machines.
C. Automation and Digitalization
- Adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies (e.g., IoT, AI, robotics) improves efficiency and reduces costs in pouch cell fabrication.
D. Sustainability
- Focus on recycling and sustainable manufacturing processes is gaining traction.
---
●8. Conclusion
Pouch cell pilot machines are essential tools for advancing battery technology and ensuring successful commercialization. They enable manufacturers to develop, test, and optimize pouch cells in a controlled and efficient manner. While challenges exist, ongoing innovations in equipment, processes, and materials continue to enhance the capabilities of these machines.
If you're planning to set up or operate a pouch cell pilot machine, carefully consider factors such as equipment specifications, environmental control, and scalability. For further details or assistance, feel free to ask!

HOT PRODUCTS
-
 Automatic Cylinderical Battery Electrode Winding Machine
Read More
Automatic Cylinderical Battery Electrode Winding Machine
Read More
-
 100-200L Double Planetary Vacuum Mixing Machine for Lithium Battery Slurry
Read More
100-200L Double Planetary Vacuum Mixing Machine for Lithium Battery Slurry
Read More
-
 Large Heating Roller Press Machine Calender For Li ion Battery Production Line
Read More
Large Heating Roller Press Machine Calender For Li ion Battery Production Line
Read More
-
 Large 3 Rollers Battery Electrode Film Intermittent Coating Machine for Pilot Production Line
Read More
Large 3 Rollers Battery Electrode Film Intermittent Coating Machine for Pilot Production Line
Read More
-
 512 Channel 5V3A Battery Grading Machine/Battery Charge Discharge Machine Tester
Read More
512 Channel 5V3A Battery Grading Machine/Battery Charge Discharge Machine Tester
Read More
 English▼
English▼




 David@battery-equipments.com
David@battery-equipments.com

