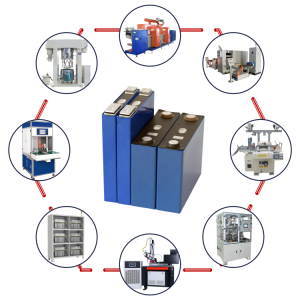
- Battery Manufacturing Equipment
- Battery Laboratory Assembly Equipment
- Battery Pack Assembly Equipment
- Sodium Ion Battery Manufacturing Equipment
- Solid State Cell Production Line
- Dry Electrode Assembly Equipment
- Supercapacitor Assembly Equipment
- Perovskite Solar Cell Lab Equipment
- Li ion Battery Materials
- Ni / Al / Cu Metal Foam
- Customized Electrode
- Cathode Active Materials
- Anode Active Materials
- Coin Cell Parts
- Lithium Chip
- Cylindrical Cell Parts
- Battery Current Collectors
- Battery Conductive Materials
- Electrolyte
- Battery Binder
- Separator and Tape
- Aluminum Laminate Film
- Nickel Strip/Foil
- Battery Tabs
- Graphene Materials
- Cu / Al / Ni / Stainless steel Foil
- Battery Laboratory Equipment
- Li ion Battery Tester
- Battery Safety Tester
- Material Characterization Tester
- Rolling Press Machine
- Electrode Mixer
- Coin Cell Crimping Machine
- Coin Cell Electrode Disc Punching
- Pouch Cell Sealing Machine
- Pouch Cell Stacking Machine
- Pouch Cell Forming Machine
- Pouch Cell Ultrasonic Welder
- Pouch Cell Electrode Die Cutter
- Cylinder Cell Sealing Machine
- Cylinder Cell Grooving Machine
- Electrode Slitting Machine
- Cylinder Cell Winding Machine
- Cylinder Cell Spot Welding Machine
- Electrolyte Filling
- Type Test Cell
- Other Battery Making Machine
- NMP Solvent Treatment System
- Vacuum Glove Box
- Coating Machine
- Lab Furnaces
- Ball Mill
- Laboratory Press
- Laboratory Equipment
- Press Equipment
- 2024-12-06
A battery fabrication plant is a facility dedicated to manufacturing energy storage systems such as lithium-ion batteries, solid-state batteries, or other advanced technologies. These plants play a vital role in industries like electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and consumer electronics.
This article outlines the key components, processes, and considerations involved in setting up and operating a battery fabrication plant.
## Core Components of a Battery Production Line
1. Raw Material Preparation
- Involves the procurement and processing of active materials (e.g., lithium compounds, nickel, cobalt, and graphite) for electrodes.
- Facilities often include mixing and drying systems to prepare electrode slurries.
2. Electrode Manufacturing
- Processes include coating, calendaring, and cutting to create high-quality anodes and cathodes.
- Key Equipment:
- Electrode coating machines.
- Calendaring machines for thickness uniformity.
- Electrode cutting systems.
3. Cell Assembly
- The assembly process varies based on cell type (pouch, cylindrical, or prismatic):
- Stacking or Winding: Aligning anodes, cathodes, and separators.
- Electrolyte Filling: Injecting precise amounts of electrolyte.
- Key Equipment:
- Winding/stacking machines.
- Vacuum sealing machines.
- Automated electrolyte dispensers.
4. Formation and Aging
- Cells undergo initial charging and discharging cycles to stabilize internal chemistry.
- Equipment: Formation racks and environmental chambers for temperature-controlled cycling.
5. Battery Module and Pack Assembly
- Integrates individual cells into modules and packs with protection systems.
- Includes welding and assembly for electrical connections and thermal management systems.
6. Testing and Quality Control
- Ensures each cell, module, and pack meets safety and performance standards.
- Testing Methods: Electrical capacity, cycle life, thermal stability, and safety tests.
## Key Equipment in a Battery Fabrication Plant
● 1. Electrode Production Equipment
- Slurry Mixers: Uniformly mix active materials, binders, and solvents.
- Coating Machines: Apply active material slurry onto current collectors.
- Drying Ovens: Evaporate solvents after coating.
- Calendaring Machines: Compress electrodes for consistent thickness.
● 2. Cell Assembly Machines
- Electrode Cutting Machines: Precisely cut electrodes for stacking or winding.
- Stacking/Winding Machines: Assemble electrodes and separators into desired configurations.
- Electrolyte Filling Machines: Dispense electrolyte under controlled conditions.
- Vacuum Sealing Machines: Create airtight seals for pouch or prismatic cells.
● 3. Formation and Aging Systems
- Used to perform initial charging cycles and stabilize cell performance.
- Includes formation racks and aging cabinets.
● 4. Automation and Robotics
- Enhances efficiency and precision in assembly lines.
- Reduces human error in electrode handling, stacking, and sealing.
● 5. Safety and Environmental Controls
- Dry Rooms: Maintain low humidity for lithium-ion battery production.
- Air Filtration Systems: Minimize contamination.
- Explosion-Proof Chambers: Ensure safety during testing and handling flammable materials.
## Steps to Set Up a Battery Fabrication Plant
1. Define Product and Technology
- Determine the battery type (e.g., lithium-ion, solid-state, or flow battery) and application (e.g., EVs, grid storage).
2. Choose a Suitable Location
- Consider factors like proximity to raw materials, skilled labor, transportation, and regulatory compliance.
3. Design the Facility Layout
- Optimize for workflow efficiency, material handling, and safety compliance.
- Include dedicated zones for raw material storage, electrode production, cell assembly, and testing.
4. Invest in Advanced Equipment
- Prioritize precision and scalability to meet demand.
5. Implement Quality Control Systems
- Ensure every stage of production adheres to strict standards.
6. Train Personnel
- Skilled workers are critical for maintaining quality and operational efficiency.
7. Adopt Sustainable Practices
- Use renewable energy sources and minimize waste to align with environmental goals.
## Applications of Batteries Manufactured in Fabrication Plants
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Batteries for cars, buses, trucks, and two-wheelers.
2. Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
- Stationary batteries for solar and wind energy storage.
3. Consumer Electronics
- Powering smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices.
4. Aerospace and Defense
- High-performance batteries for satellites and military applications.
## Challenges in Battery Fabrication Plants
1. Raw Material Sourcing
- Dependence on critical materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
2. Cost Management
- Balancing equipment costs and production scalability.
3. Environmental Regulations
- Complying with stringent rules for emissions and waste management.
4. Technological Advancements
- Staying competitive requires continuous innovation.
5. Energy Efficiency
- Optimizing energy use in production processes.
## Conclusion
A battery fabrication plant is a cornerstone of the energy transition, enabling advancements in electric mobility, renewable energy storage, and portable electronics. By leveraging cutting-edge equipment, automation, and quality control, manufacturers can produce reliable, high-performance batteries to meet growing global demand. Strategic planning, skilled personnel, and sustainable practices are critical for success in this rapidly evolving industry.
-
 Automatic Cylinderical Battery Electrode Winding Machine
Read More
Automatic Cylinderical Battery Electrode Winding Machine
Read More
-
 100-200L Double Planetary Vacuum Mixing Machine for Lithium Battery Slurry
Read More
100-200L Double Planetary Vacuum Mixing Machine for Lithium Battery Slurry
Read More
-
 Large Heating Roller Press Machine Calender For Li ion Battery Production Line
Read More
Large Heating Roller Press Machine Calender For Li ion Battery Production Line
Read More
-
 Large 3 Rollers Battery Electrode Film Intermittent Coating Machine for Pilot Production Line
Read More
Large 3 Rollers Battery Electrode Film Intermittent Coating Machine for Pilot Production Line
Read More
-
 512 Channel 5V3A Battery Grading Machine/Battery Charge Discharge Machine Tester
Read More
512 Channel 5V3A Battery Grading Machine/Battery Charge Discharge Machine Tester
Read More
 English▼
English▼




 David@battery-equipments.com
David@battery-equipments.com

